By Annie Keller
Published November 23, 2020
The possibilities involved in stem cell research have long fascinated both the public and workers in the medical field. Here are just a few of the most recent innovations in stem cell research.
Induced pluripotent stem cells, stem cells produced from somatic tissue, are one of the most promising types of stem cells for research. However, it is difficult to differentiate the cells to become whatever tissue is needed. Recently, researchers at the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden at TU Dresden and University of Bonn in Germany and at Harvard University have discovered a way to extract the different cells by using a transcription factor. Researchers insert the DNA sequence of the transcription factor into the cell genome, and as the cells mature, researchers can search for the marker and select stem cells that have it.
A drug that can help lure stem cells to heal damaged tissue has been discovered. Evan Snyder, MD, director of the Center for Stem Cells & Regenerative Medicine at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute, worked on the discovery with several colleagues. The drug, SDV1a, enhances the binding of stem cells at sites of inflammation while minimizing the risk of increasing inflammation. An initial trial has been planned for ALS (Lou Gherig’s disease), and SDV1a may prove useful in treating other neurodegenerative conditions,
In 2019, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine began a trial of a potential treatment using stems cells for sickle cell anemia. Stem cells taken from the patient are genetically modified to correct the gene that causes blood cells to easily form the sickle shape and re-injected into the patient. One recipient of this new therapy found that 70% of his blood cells carried the corrected gene following 3 months of treatment.
Stem cell research will likely continue to innovate as more ways of using stem cells are studied, and stem cell therapy remains an area of great interest. Heart disease, arthritis, and many different types of cancer are just a few of the many conditions that are awaiting stem cell treatment.
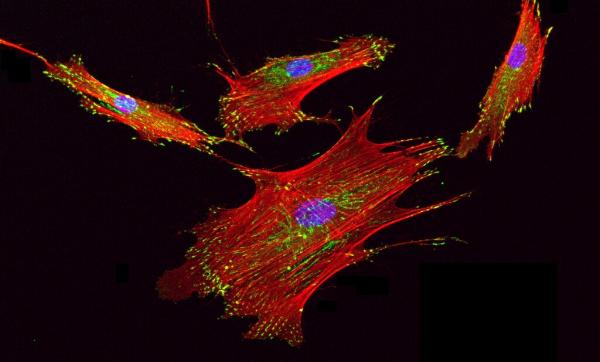
Image source: “Focal Adhesions in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells” by National Institutes of Health (NIH) is licensed under CC BY-NC 2.0

 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post